799. Champagne Tower
Medium
We stack glasses in a pyramid, where the first row has 1 glass, the second row has 2 glasses, and so on until the 100th row. Each glass holds one cup of champagne.
Then, some champagne is poured into the first glass at the top. When the topmost glass is full, any excess liquid poured will fall equally to the glass immediately to the left and right of it. When those glasses become full, any excess champagne will fall equally to the left and right of those glasses, and so on. (A glass at the bottom row has its excess champagne fall on the floor.)
+ +For example, after one cup of champagne is poured, the top most glass is full. After two cups of champagne are poured, the two glasses on the second row are half full. After three cups of champagne are poured, those two cups become full - there are 3 full glasses total now. After four cups of champagne are poured, the third row has the middle glass half full, and the two outside glasses are a quarter full, as pictured below.
+ +
Now after pouring some non-negative integer cups of champagne, return how full the jth glass in the ith row is (both i and j are 0-indexed.)
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: poured = 1, query_row = 1, query_glass = 1 +Output: 0.00000 +Explanation: We poured 1 cup of champange to the top glass of the tower (which is indexed as (0, 0)). There will be no excess liquid so all the glasses under the top glass will remain empty. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: poured = 2, query_row = 1, query_glass = 1 +Output: 0.50000 +Explanation: We poured 2 cups of champange to the top glass of the tower (which is indexed as (0, 0)). There is one cup of excess liquid. The glass indexed as (1, 0) and the glass indexed as (1, 1) will share the excess liquid equally, and each will get half cup of champange. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: poured = 100000009, query_row = 33, query_glass = 17 +Output: 1.00000 ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= poured <= 109
+ 0 <= query_glass <= query_row < 100
+
389. Find the Difference
Easy
You are given two strings s and t.
String t is generated by random shuffling string s and then add one more letter at a random position.
Return the letter that was added to t.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "abcd", t = "abcde" +Output: "e" +Explanation: 'e' is the letter that was added. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "", t = "y" +Output: "y" ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= s.length <= 1000
+ t.length == s.length + 1
+ sandtconsist of lowercase English letters.
+
389. Find the Difference
Easy
You are given two strings s and t.
String t is generated by random shuffling string s and then add one more letter at a random position.
Return the letter that was added to t.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "abcd", t = "abcde" +Output: "e" +Explanation: 'e' is the letter that was added. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "", t = "y" +Output: "y" ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= s.length <= 1000
+ t.length == s.length + 1
+ sandtconsist of lowercase English letters.
+
Thank you for consistently taking part in the POTD.
Feel free to share your feedback and suggestions by filling up the Form below.
https://forms.gle/Ga6fVJBzEtDSvEop9
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Given two integer array A and B of size N each.
A sum combination is made by adding one element from array A and another element of array B.
Return the maximum K valid sum combinations from all the possible sum combinations.
Note : Output array must be sorted in non-increasing order.
+Example 1:
+Input:
N = 2
K = 2
A [ ] = {3, 2}
B [ ] = {1, 4}
Output: {7, 6}
Explanation:
7 -> (A : 3) + (B : 4)
6 -> (A : 2) + (B : 4)
+Example 2:
+Input:
N = 4
K = 3
A [ ] = {1, 4, 2, 3}
B [ ] = {2, 5, 1, 6}
Output: {10, 9, 9}
Explanation:
10 -> (A : 4) + (B : 6)
9 -> (A : 4) + (B : 5)
9 -> (A : 3) + (B : 6)
+Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function maxCombinations() which takes the interger N,integer K and two integer arrays A [ ] and B [ ] as parameters and returns the maximum K valid distinct sum combinations .
Expected Time Complexity: O(Nlog(N))
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Constraints:
1 ≤ N ≤ 105
1 ≤ K ≤ N
1 ≤ A [ i ] , B [ i ] ≤ 104
792. Number of Matching Subsequences
Medium
Given a string s and an array of strings words, return the number of words[i] that is a subsequence of s.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
+ +-
+
- For example,
"ace"is a subsequence of"abcde".
+
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "abcde", words = ["a","bb","acd","ace"] +Output: 3 +Explanation: There are three strings in words that are a subsequence of s: "a", "acd", "ace". ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "dsahjpjauf", words = ["ahjpjau","ja","ahbwzgqnuk","tnmlanowax"] +Output: 2 ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
+ 1 <= words.length <= 5000
+ 1 <= words[i].length <= 50
+ sandwords[i]consist of only lowercase English letters.
+
316. Remove Duplicate Letters
Medium
Given a string s, remove duplicate letters so that every letter appears once and only once. You must make sure your result is the smallest in lexicographical order among all possible results.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "bcabc" +Output: "abc" ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "cbacdcbc" +Output: "acdb" ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length <= 104
+ sconsists of lowercase English letters.
+
+
Note: This question is the same as 1081: https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subsequence-of-distinct-characters/
+1081. Smallest Subsequence of Distinct Characters
Medium
Given a string s, return the lexicographically smallest subsequence of s that contains all the distinct characters of s exactly once.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "bcabc" +Output: "abc" ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "cbacdcbc" +Output: "acdb" ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length <= 1000
+ sconsists of lowercase English letters.
+
+Note: This question is the same as 316: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicate-letters/
1081. Smallest Subsequence of Distinct Characters
Medium
Given a string s, return the lexicographically smallest subsequence of s that contains all the distinct characters of s exactly once.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "bcabc" +Output: "abc" ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "cbacdcbc" +Output: "acdb" ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length <= 1000
+ sconsists of lowercase English letters.
+
+Note: This question is the same as 316: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicate-letters/
880. Decoded String at Index
Medium
You are given an encoded string s. To decode the string to a tape, the encoded string is read one character at a time and the following steps are taken:
-
+
- If the character read is a letter, that letter is written onto the tape. +
- If the character read is a digit
d, the entire current tape is repeatedly writtend - 1more times in total.
+
Given an integer k, return the kth letter (1-indexed) in the decoded string.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "leet2code3", k = 10 +Output: "o" +Explanation: The decoded string is "leetleetcodeleetleetcodeleetleetcode". +The 10th letter in the string is "o". ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "ha22", k = 5 +Output: "h" +Explanation: The decoded string is "hahahaha". +The 5th letter is "h". ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: s = "a2345678999999999999999", k = 1 +Output: "a" +Explanation: The decoded string is "a" repeated 8301530446056247680 times. +The 1st letter is "a". ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= s.length <= 100
+ sconsists of lowercase English letters and digits2through9.
+ sstarts with a letter.
+ 1 <= k <= 109
+ - It is guaranteed that
kis less than or equal to the length of the decoded string.
+ - The decoded string is guaranteed to have less than
263letters.
+
Given a sorted array arr[] of distinct integers. Sort the array into a wave-like array(In Place).
In other words, arrange the elements into a sequence such that arr[1] >= arr[2] <= arr[3] >= arr[4] <= arr[5].....
If there are multiple solutions, find the lexicographically smallest one.
+Note:The given array is sorted in ascending order, and you don't need to return anything to make changes in the original array itself.
+Example 1:
+Input:
+n = 5
+arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5}
+Output: 2 1 4 3 5
+Explanation: Array elements after
+sorting it in wave form are
+2 1 4 3 5.
+Example 2:
+Input:
+n = 6
+arr[] = {2,4,7,8,9,10}
+Output: 4 2 8 7 10 9
+Explanation: Array elements after
+sorting it in wave form are
+4 2 8 7 10 9.
+Your Task:
The task is to complete the function convertToWave(), which converts the given array to a wave array.
Expected Time Complexity: O(n).
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Constraints:
1 ≤ n ≤ 106
0 ≤ arr[i] ≤107
896. Monotonic Array
Easy
An array is monotonic if it is either monotone increasing or monotone decreasing.
+ +An array nums is monotone increasing if for all i <= j, nums[i] <= nums[j]. An array nums is monotone decreasing if for all i <= j, nums[i] >= nums[j].
Given an integer array nums, return true if the given array is monotonic, or false otherwise.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,2,3] +Output: true ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [6,5,4,4] +Output: true ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [1,3,2] +Output: false ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 105
+ -105 <= nums[i] <= 105
+
You are given an n x m binary matrix grid, where 0 represents a sea cell and 1 represents a land cell.
+A move consists of walking from one land cell to another adjacent (4-directionally) land cell or walking off the boundary of the grid.
+Find the number of land cells in grid for which we cannot walk off the boundary of the grid in any number of moves.
+Example 1:
+Input: +grid[][] = {{0, 0, 0, 0}, + {1, 0, 1, 0}, + {0, 1, 1, 0}, + {0, 0, 0, 0}} +Output: +3 +Explanation: +0 0 0 0 +1 0 1 0 +0 1 1 0 +0 0 0 0 +The highlighted cells represents the land cells. ++
Example 2:
+Input: +grid[][] = {{0, 0, 0, 1}, + {0, 1, 1, 0}, + {0, 1, 1, 0}, + {0, 0, 0, 1}, + {0, 1, 1, 0}} +Output: +4 +Explanation: +0 0 0 1 +0 1 1 0 +0 1 1 0 +0 0 0 1 +0 1 1 0 +The highlighted cells represents the land cells.+
Your Task:
+You don't need to print or input anything. Complete the function numberOfEnclaves() which takes a 2D integer matrix grid as the input parameter and returns an integer, denoting the number of land cells.
+Expected Time Complexity: O(n * m)
+Expected Space Complexity: O(n * m)
+Constraints:
+-
+
- 1 <= n, m <= 500 +
- grid[i][j] == 0 or 1 +
456. 132 Pattern
Medium
Given an array of n integers nums, a 132 pattern is a subsequence of three integers nums[i], nums[j] and nums[k] such that i < j < k and nums[i] < nums[k] < nums[j].
Return true if there is a 132 pattern in nums, otherwise, return false.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3,4] +Output: false +Explanation: There is no 132 pattern in the sequence. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [3,1,4,2] +Output: true +Explanation: There is a 132 pattern in the sequence: [1, 4, 2]. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [-1,3,2,0] +Output: true +Explanation: There are three 132 patterns in the sequence: [-1, 3, 2], [-1, 3, 0] and [-1, 2, 0]. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
n == nums.length
+ 1 <= n <= 2 * 105
+ -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
456. 132 Pattern
Medium
Given an array of n integers nums, a 132 pattern is a subsequence of three integers nums[i], nums[j] and nums[k] such that i < j < k and nums[i] < nums[k] < nums[j].
Return true if there is a 132 pattern in nums, otherwise, return false.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3,4] +Output: false +Explanation: There is no 132 pattern in the sequence. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [3,1,4,2] +Output: true +Explanation: There is a 132 pattern in the sequence: [1, 4, 2]. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [-1,3,2,0] +Output: true +Explanation: There are three 132 patterns in the sequence: [-1, 3, 2], [-1, 3, 0] and [-1, 2, 0]. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
n == nums.length
+ 1 <= n <= 2 * 105
+ -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
Given a boolean matrix of size RxC where each cell contains either 0 or 1, modify it such that if a matrix cell matrix[i][j] is 1 then all the cells in its ith row and jth column will become 1.
+Example 1:
+Input: +R = 2, C = 2 +matrix[][] = {{1, 0}, + {0, 0}} +Output: +1 1 +1 0 +Explanation: +Only cell that has 1 is at (0,0) so all +cells in row 0 are modified to 1 and all +cells in column 0 are modified to 1.+
Example 2:
Input: +R = 4, C = 3 +matrix[][] = {{ 1, 0, 0}, + { 1, 0, 0}, + { 1, 0, 0}, + { 0, 0, 0}} +Output: +1 1 1 +1 1 1 +1 1 1 +1 0 0 +Explanation: +The position of cells that have 1 in +the original matrix are (0,0), (1,0) +and (2,0). Therefore, all cells in row +0,1,2 are and column 0 are modified to 1.+
Your Task:
You dont need to read input or print anything. Complete the function booleanMatrix() that takes the matrix as input parameter and modifies it in-place.
Expected Time Complexity: O(R * C)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(R + C)
Constraints:
1 ≤ R, C ≤ 1000
0 ≤ matrix[i][j] ≤ 1
557. Reverse Words in a String III
Easy
Given a string s, reverse the order of characters in each word within a sentence while still preserving whitespace and initial word order.
+
Example 1:
+Input: s = "Let's take LeetCode contest" +Output: "s'teL ekat edoCteeL tsetnoc" +
Example 2:
+Input: s = "God Ding" +Output: "doG gniD" ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
+ scontains printable ASCII characters.
+ sdoes not contain any leading or trailing spaces.
+ - There is at least one word in
s.
+ - All the words in
sare separated by a single space.
+
557. Reverse Words in a String III
Easy
Given a string s, reverse the order of characters in each word within a sentence while still preserving whitespace and initial word order.
+
Example 1:
+Input: s = "Let's take LeetCode contest" +Output: "s'teL ekat edoCteeL tsetnoc" +
Example 2:
+Input: s = "God Ding" +Output: "doG gniD" ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
+ scontains printable ASCII characters.
+ sdoes not contain any leading or trailing spaces.
+ - There is at least one word in
s.
+ - All the words in
sare separated by a single space.
+
2876. Count Visited Nodes in a Directed Graph
Hard
There is a directed graph consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and n directed edges.
You are given a 0-indexed array edges where edges[i] indicates that there is an edge from node i to node edges[i].
Consider the following process on the graph:
+ +-
+
- You start from a node
xand keep visiting other nodes through edges until you reach a node that you have already visited before on this same process.
+
Return an array answer where answer[i] is the number of different nodes that you will visit if you perform the process starting from node i.
+
Example 1:
+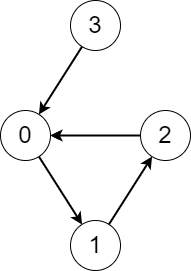 +
+Input: edges = [1,2,0,0] +Output: [3,3,3,4] +Explanation: We perform the process starting from each node in the following way: +- Starting from node 0, we visit the nodes 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0. The number of different nodes we visit is 3. +- Starting from node 1, we visit the nodes 1 -> 2 -> 0 -> 1. The number of different nodes we visit is 3. +- Starting from node 2, we visit the nodes 2 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2. The number of different nodes we visit is 3. +- Starting from node 3, we visit the nodes 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0. The number of different nodes we visit is 4. ++ +
Example 2:
+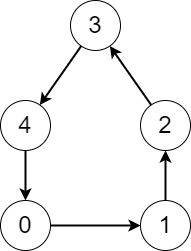 +
+Input: edges = [1,2,3,4,0] +Output: [5,5,5,5,5] +Explanation: Starting from any node we can visit every node in the graph in the process. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
n == edges.length
+ 2 <= n <= 105
+ 0 <= edges[i] <= n - 1
+ edges[i] != i
+
You are given a matrix of dimensions n x m. The task is to perform boundary traversal on the matrix in a clockwise manner.
Example 1:
Input:
+n = 4, m = 4
+matrix[][] = {{1, 2, 3, 4},
+ {5, 6, 7, 8},
+ {9, 10, 11, 12},
+ {13, 14, 15,16}}
+Output: 1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5
+Explanation:
+The matrix is:
+1 2 3 4
+5 6 7 8
+9 10 11 12
+13 14 15 16
+The boundary traversal is:
+1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+n = 3, m = 4
+matrrix[][] = {{12, 11, 10, 9},
+ {8, 7, 6, 5},
+ {4, 3, 2, 1}}
+Output: 12 11 10 9 5 1 2 3 4 8
+
+Your Task:
Complete the function boundaryTraversal() that takes matrix, n and m as input parameters and returns the list of integers that form the boundary traversal of the matrix in a clockwise manner.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N + M)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
1 <= n, m<= 1000
0 <= matrixi <= 1000
2038. Remove Colored Pieces if Both Neighbors are the Same Color
Medium
There are n pieces arranged in a line, and each piece is colored either by 'A' or by 'B'. You are given a string colors of length n where colors[i] is the color of the ith piece.
Alice and Bob are playing a game where they take alternating turns removing pieces from the line. In this game, Alice moves first.
+ +-
+
- Alice is only allowed to remove a piece colored
'A'if both its neighbors are also colored'A'. She is not allowed to remove pieces that are colored'B'.
+ - Bob is only allowed to remove a piece colored
'B'if both its neighbors are also colored'B'. He is not allowed to remove pieces that are colored'A'.
+ - Alice and Bob cannot remove pieces from the edge of the line. +
- If a player cannot make a move on their turn, that player loses and the other player wins. +
Assuming Alice and Bob play optimally, return true if Alice wins, or return false if Bob wins.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: colors = "AAABABB" +Output: true +Explanation: +AAABABB -> AABABB +Alice moves first. +She removes the second 'A' from the left since that is the only 'A' whose neighbors are both 'A'. + +Now it's Bob's turn. +Bob cannot make a move on his turn since there are no 'B's whose neighbors are both 'B'. +Thus, Alice wins, so return true. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: colors = "AA" +Output: false +Explanation: +Alice has her turn first. +There are only two 'A's and both are on the edge of the line, so she cannot move on her turn. +Thus, Bob wins, so return false. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: colors = "ABBBBBBBAAA" +Output: false +Explanation: +ABBBBBBBAAA -> ABBBBBBBAA +Alice moves first. +Her only option is to remove the second to last 'A' from the right. + +ABBBBBBBAA -> ABBBBBBAA +Next is Bob's turn. +He has many options for which 'B' piece to remove. He can pick any. + +On Alice's second turn, she has no more pieces that she can remove. +Thus, Bob wins, so return false. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= colors.length <= 105
+ colorsconsists of only the letters'A'and'B'
+
2038. Remove Colored Pieces if Both Neighbors are the Same Color
Medium
There are n pieces arranged in a line, and each piece is colored either by 'A' or by 'B'. You are given a string colors of length n where colors[i] is the color of the ith piece.
Alice and Bob are playing a game where they take alternating turns removing pieces from the line. In this game, Alice moves first.
+ +-
+
- Alice is only allowed to remove a piece colored
'A'if both its neighbors are also colored'A'. She is not allowed to remove pieces that are colored'B'.
+ - Bob is only allowed to remove a piece colored
'B'if both its neighbors are also colored'B'. He is not allowed to remove pieces that are colored'A'.
+ - Alice and Bob cannot remove pieces from the edge of the line. +
- If a player cannot make a move on their turn, that player loses and the other player wins. +
Assuming Alice and Bob play optimally, return true if Alice wins, or return false if Bob wins.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: colors = "AAABABB" +Output: true +Explanation: +AAABABB -> AABABB +Alice moves first. +She removes the second 'A' from the left since that is the only 'A' whose neighbors are both 'A'. + +Now it's Bob's turn. +Bob cannot make a move on his turn since there are no 'B's whose neighbors are both 'B'. +Thus, Alice wins, so return true. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: colors = "AA" +Output: false +Explanation: +Alice has her turn first. +There are only two 'A's and both are on the edge of the line, so she cannot move on her turn. +Thus, Bob wins, so return false. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: colors = "ABBBBBBBAAA" +Output: false +Explanation: +ABBBBBBBAAA -> ABBBBBBBAA +Alice moves first. +Her only option is to remove the second to last 'A' from the right. + +ABBBBBBBAA -> ABBBBBBAA +Next is Bob's turn. +He has many options for which 'B' piece to remove. He can pick any. + +On Alice's second turn, she has no more pieces that she can remove. +Thus, Bob wins, so return false. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= colors.length <= 105
+ colorsconsists of only the letters'A'and'B'
+
1512. Number of Good Pairs
Easy
Given an array of integers nums, return the number of good pairs.
A pair (i, j) is called good if nums[i] == nums[j] and i < j.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,1,3] +Output: 4 +Explanation: There are 4 good pairs (0,3), (0,4), (3,4), (2,5) 0-indexed. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [1,1,1,1] +Output: 6 +Explanation: Each pair in the array are good. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3] +Output: 0 ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 100
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 100
+
1512. Number of Good Pairs
Easy
Given an array of integers nums, return the number of good pairs.
A pair (i, j) is called good if nums[i] == nums[j] and i < j.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,1,3] +Output: 4 +Explanation: There are 4 good pairs (0,3), (0,4), (3,4), (2,5) 0-indexed. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [1,1,1,1] +Output: 6 +Explanation: Each pair in the array are good. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3] +Output: 0 ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 100
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 100
+
Given a positive integer, return its corresponding column title as appear in an Excel sheet.
Excel columns has a pattern like A, B, C, … ,Z, AA, AB, AC,…. ,AZ, BA, BB, … ZZ, AAA, AAB ….. etc. In other words, column 1 is named as “A”, column 2 as “B”, column 27 as “AA” and so on.
Example 1:
+Input:
+N = 28
+Output: AB
+Explanation: 1 to 26 are A to Z.
+Then, 27 is AA and 28 = AB.
+
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+N = 13
+Output: M
+Explanation: M is the 13th character of
+alphabet.
+
+Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function colName() which takes the column number N as input and returns the column name represented as a string.
Expected Time Complexity: O(LogN).
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Constraints:
1 <= N <= 1018
706. Design HashMap
Easy
Design a HashMap without using any built-in hash table libraries.
+ +Implement the MyHashMap class:
-
+
MyHashMap()initializes the object with an empty map.
+ void put(int key, int value)inserts a(key, value)pair into the HashMap. If thekeyalready exists in the map, update the correspondingvalue.
+ int get(int key)returns thevalueto which the specifiedkeyis mapped, or-1if this map contains no mapping for thekey.
+ void remove(key)removes thekeyand its correspondingvalueif the map contains the mapping for thekey.
+
+
Example 1:
+ +Input +["MyHashMap", "put", "put", "get", "get", "put", "get", "remove", "get"] +[[], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3], [2, 1], [2], [2], [2]] +Output +[null, null, null, 1, -1, null, 1, null, -1] + +Explanation +MyHashMap myHashMap = new MyHashMap(); +myHashMap.put(1, 1); // The map is now [[1,1]] +myHashMap.put(2, 2); // The map is now [[1,1], [2,2]] +myHashMap.get(1); // return 1, The map is now [[1,1], [2,2]] +myHashMap.get(3); // return -1 (i.e., not found), The map is now [[1,1], [2,2]] +myHashMap.put(2, 1); // The map is now [[1,1], [2,1]] (i.e., update the existing value) +myHashMap.get(2); // return 1, The map is now [[1,1], [2,1]] +myHashMap.remove(2); // remove the mapping for 2, The map is now [[1,1]] +myHashMap.get(2); // return -1 (i.e., not found), The map is now [[1,1]] ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= key, value <= 106
+ - At most
104calls will be made toput,get, andremove.
+
706. Design HashMap
Easy
Design a HashMap without using any built-in hash table libraries.
+ +Implement the MyHashMap class:
-
+
MyHashMap()initializes the object with an empty map.
+ void put(int key, int value)inserts a(key, value)pair into the HashMap. If thekeyalready exists in the map, update the correspondingvalue.
+ int get(int key)returns thevalueto which the specifiedkeyis mapped, or-1if this map contains no mapping for thekey.
+ void remove(key)removes thekeyand its correspondingvalueif the map contains the mapping for thekey.
+
+
Example 1:
+ +Input +["MyHashMap", "put", "put", "get", "get", "put", "get", "remove", "get"] +[[], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3], [2, 1], [2], [2], [2]] +Output +[null, null, null, 1, -1, null, 1, null, -1] + +Explanation +MyHashMap myHashMap = new MyHashMap(); +myHashMap.put(1, 1); // The map is now [[1,1]] +myHashMap.put(2, 2); // The map is now [[1,1], [2,2]] +myHashMap.get(1); // return 1, The map is now [[1,1], [2,2]] +myHashMap.get(3); // return -1 (i.e., not found), The map is now [[1,1], [2,2]] +myHashMap.put(2, 1); // The map is now [[1,1], [2,1]] (i.e., update the existing value) +myHashMap.get(2); // return 1, The map is now [[1,1], [2,1]] +myHashMap.remove(2); // remove the mapping for 2, The map is now [[1,1]] +myHashMap.get(2); // return -1 (i.e., not found), The map is now [[1,1]] ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= key, value <= 106
+ - At most
104calls will be made toput,get, andremove.
+
343. Integer Break
Medium
Given an integer n, break it into the sum of k positive integers, where k >= 2, and maximize the product of those integers.
Return the maximum product you can get.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: n = 2 +Output: 1 +Explanation: 2 = 1 + 1, 1 × 1 = 1. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: n = 10 +Output: 36 +Explanation: 10 = 3 + 3 + 4, 3 × 3 × 4 = 36. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= n <= 58
+
343. Integer Break
Medium
Given an integer n, break it into the sum of k positive integers, where k >= 2, and maximize the product of those integers.
Return the maximum product you can get.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: n = 2 +Output: 1 +Explanation: 2 = 1 + 1, 1 × 1 = 1. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: n = 10 +Output: 36 +Explanation: 10 = 3 + 3 + 4, 3 × 3 × 4 = 36. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= n <= 58
+
Given a linked list, you have to perform the following task:
+-
+
- Extract the alternative nodes starting from second node. +
- Reverse the extracted list. +
- Append the extracted list at the end of the original list. +
Note: Try to solve the problem without using any extra memory.
+Example 1:
+Input:
+LinkedList = 10->4->9->1->3->5->9->4
+Output:
10 9 3 9 4 5 1 4
+Explanation:
Alternative nodes in the given linked list are 4,1,5,4. Reversing the alternative nodes from the given list, and then appending them to the end of the list results in a list 10->9->3->9->4->5->1->4.
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+LinkedList = 1->2->3->4->5
+Output:
1 3 5 4 2
+Explanation:
Alternative nodes in the given linked list are 2 and 4. Reversing the alternative nodes from the given list, and then appending them to the end of the list results in a list 1->3->5->4->2.
+Your Task:
You don't have to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function rearrange() which takes the head of the linked list as input and rearranges the list as required.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
1 <= N <= 105
0 <= Node_value <= 109
Given a singly linked list of size N. The task is to swap elements in the linked list pairwise.
For example, if the input list is 1 2 3 4, the resulting list after swaps will be 2 1 4 3.
Note: You need to swap the nodes, not only the data. If only data is swapped then driver will print -1.
Example 1:
+Input:
+LinkedList: 1->2->2->4->5->6->7->8
+Output:
2 1 4 2 6 5 8 7
+Explanation:
After swapping each pair considering (1,2), (2, 4), (5, 6).. so on as pairs, we get 2, 1, 4, 2, 6, 5, 8, 7 as a new linked list.
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+LinkedList: 1->3->4->7->9->10->1
+Output:
3 1 7 4 10 9 1
+Explanation:
After swapping each pair considering (1,3), (4, 7), (9, 10).. so on as pairs, we get 3, 1, 7, 4, 10, 9, 1 as a new linked list.
+Your Task:
The task is to complete the function pairWiseSwap() which takes the head node as the only argument and returns the head of modified linked list.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N).
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Constraints:
1 ≤ N ≤ 105
1420. Build Array Where You Can Find The Maximum Exactly K Comparisons
Hard
You are given three integers n, m and k. Consider the following algorithm to find the maximum element of an array of positive integers:
 +
+You should build the array arr which has the following properties:
+ +-
+
arrhas exactlynintegers.
+ 1 <= arr[i] <= mwhere(0 <= i < n).
+ - After applying the mentioned algorithm to
arr, the valuesearch_costis equal tok.
+
Return the number of ways to build the array arr under the mentioned conditions. As the answer may grow large, the answer must be computed modulo 109 + 7.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: n = 2, m = 3, k = 1 +Output: 6 +Explanation: The possible arrays are [1, 1], [2, 1], [2, 2], [3, 1], [3, 2] [3, 3] ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: n = 5, m = 2, k = 3 +Output: 0 +Explanation: There are no possible arrays that satisify the mentioned conditions. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: n = 9, m = 1, k = 1 +Output: 1 +Explanation: The only possible array is [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= n <= 50
+ 1 <= m <= 100
+ 0 <= k <= n
+
Given a linked list sorted in ascending order and an integer called data, insert data in the linked list such that the list remains sorted.
+Example 1:
+Input: +LinkedList: 25->36->47->58->69->80 +data: 19 +Output:+
19 25 36 47 58 69 80
Explanation:
After inserting 19 the sorted linked list will look like the one in the output.
Example 2:
+Input:
+LinkedList: 50->100
+data: 75
+Output:
50 75 100
Explanation:
After inserting 75 the sorted linked list will look like the one in the output.
+Your Task:
The task is to complete the function sortedInsert() which should insert the element in sorted Linked List and return the head of the linked list
Expected Time Complexity: O(N).
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Constraints:
1 <= N <= 104
-99999 <= A[i] <= 99999, for each valid i
1458. Max Dot Product of Two Subsequences
Hard
Given two arrays nums1 and nums2.
Return the maximum dot product between non-empty subsequences of nums1 and nums2 with the same length.
+ +A subsequence of a array is a new array which is formed from the original array by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, [2,3,5] is a subsequence of [1,2,3,4,5] while [1,5,3] is not).
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums1 = [2,1,-2,5], nums2 = [3,0,-6] +Output: 18 +Explanation: Take subsequence [2,-2] from nums1 and subsequence [3,-6] from nums2. +Their dot product is (2*3 + (-2)*(-6)) = 18.+ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums1 = [3,-2], nums2 = [2,-6,7] +Output: 21 +Explanation: Take subsequence [3] from nums1 and subsequence [7] from nums2. +Their dot product is (3*7) = 21.+ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums1 = [-1,-1], nums2 = [1,1] +Output: -1 +Explanation: Take subsequence [-1] from nums1 and subsequence [1] from nums2. +Their dot product is -1.+ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 500
+ -1000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 1000
+
1458. Max Dot Product of Two Subsequences
Hard
Given two arrays nums1 and nums2.
Return the maximum dot product between non-empty subsequences of nums1 and nums2 with the same length.
+ +A subsequence of a array is a new array which is formed from the original array by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, [2,3,5] is a subsequence of [1,2,3,4,5] while [1,5,3] is not).
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums1 = [2,1,-2,5], nums2 = [3,0,-6] +Output: 18 +Explanation: Take subsequence [2,-2] from nums1 and subsequence [3,-6] from nums2. +Their dot product is (2*3 + (-2)*(-6)) = 18.+ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums1 = [3,-2], nums2 = [2,-6,7] +Output: 21 +Explanation: Take subsequence [3] from nums1 and subsequence [7] from nums2. +Their dot product is (3*7) = 21.+ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums1 = [-1,-1], nums2 = [1,1] +Output: -1 +Explanation: Take subsequence [-1] from nums1 and subsequence [1] from nums2. +Their dot product is -1.+ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 500
+ -1000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 1000
+
34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array
Medium
Given an array of integers nums sorted in non-decreasing order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
If target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
+
Example 1:
+Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8 +Output: [3,4] +
Example 2:
+Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6 +Output: [-1,-1] +
Example 3:
+Input: nums = [], target = 0 +Output: [-1,-1] ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= nums.length <= 105
+ -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+ numsis a non-decreasing array.
+ -109 <= target <= 109
+
34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array
Medium
Given an array of integers nums sorted in non-decreasing order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
If target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
+
Example 1:
+Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8 +Output: [3,4] +
Example 2:
+Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6 +Output: [-1,-1] +
Example 3:
+Input: nums = [], target = 0 +Output: [-1,-1] ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= nums.length <= 105
+ -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+ numsis a non-decreasing array.
+ -109 <= target <= 109
+
Given a binary tree, find its height.
+Example 1:
+Input:
+ 1
+ / \
+ 2 3
+Output: 2
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+ 2
+ \
+ 1
+ /
+ 3
+Output: 3
+Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function height() which takes root node of the tree as input parameter and returns an integer denoting the height of the tree. If the tree is empty, return 0.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Constraints:
1 <= Number of nodes <= 105
1 <= Data of a node <= 109
2009. Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array Continuous
Hard
You are given an integer array nums. In one operation, you can replace any element in nums with any integer.
nums is considered continuous if both of the following conditions are fulfilled:
-
+
- All elements in
numsare unique.
+ - The difference between the maximum element and the minimum element in
numsequalsnums.length - 1.
+
For example, nums = [4, 2, 5, 3] is continuous, but nums = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6] is not continuous.
Return the minimum number of operations to make nums continuous.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [4,2,5,3] +Output: 0 +Explanation: nums is already continuous. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [1,2,3,5,6] +Output: 1 +Explanation: One possible solution is to change the last element to 4. +The resulting array is [1,2,3,5,4], which is continuous. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [1,10,100,1000] +Output: 3 +Explanation: One possible solution is to: +- Change the second element to 2. +- Change the third element to 3. +- Change the fourth element to 4. +The resulting array is [1,2,3,4], which is continuous. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 105
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
Given a binary tree, find if it is height balanced or not.
A tree is height balanced if difference between heights of left and right subtrees is not more than one for all nodes of tree.
A height balanced tree
1
/ \
10 39
/
5
An unbalanced tree
1
/
10
/
5
Example 1:
+Input:
+ 1
+ /
+ 2
+ \
+ 3
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The max difference in height
+of left subtree and right subtree is 2,
+which is greater than 1. Hence unbalanced
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+ 10
+ / \
+ 20 30
+ / \
+ 40 60
+Output: 1
+Explanation: The max difference in height
+of left subtree and right subtree is 1.
+Hence balanced.
+
+Your Task:
You don't need to take input. Just complete the function isBalanced() that takes root node as parameter and returns true, if the tree is balanced else returns false.
Constraints:
1 <= Number of nodes <= 105
1 <= Data of a node <= 109
Expected time complexity: O(N)
Expected auxiliary space: O(h) , where h = height of tree
2251. Number of Flowers in Full Bloom
Hard
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array flowers, where flowers[i] = [starti, endi] means the ith flower will be in full bloom from starti to endi (inclusive). You are also given a 0-indexed integer array people of size n, where people[i] is the time that the ith person will arrive to see the flowers.
Return an integer array answer of size n, where answer[i] is the number of flowers that are in full bloom when the ith person arrives.
+
Example 1:
+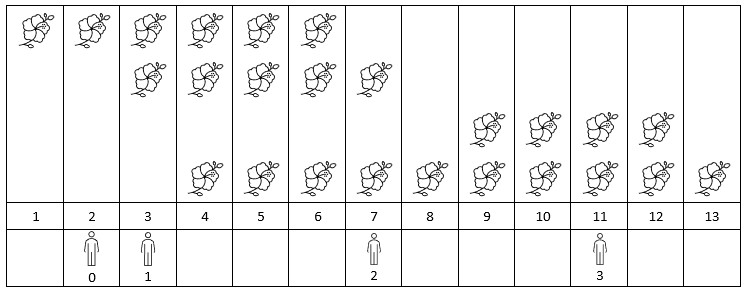 +
+Input: flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], poeple = [2,3,7,11] +Output: [1,2,2,2] +Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. +For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival. ++ +
Example 2:
+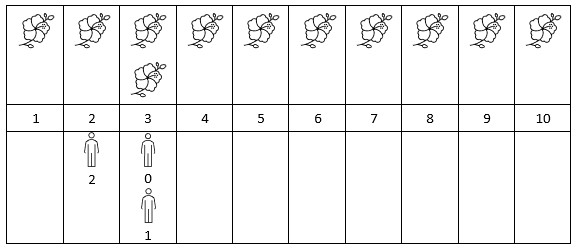 +
+Input: flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], poeple = [3,3,2] +Output: [2,2,1] +Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. +For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104
+ flowers[i].length == 2
+ 1 <= starti <= endi <= 109
+ 1 <= people.length <= 5 * 104
+ 1 <= people[i] <= 109
+
2251. Number of Flowers in Full Bloom
Hard
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array flowers, where flowers[i] = [starti, endi] means the ith flower will be in full bloom from starti to endi (inclusive). You are also given a 0-indexed integer array people of size n, where people[i] is the time that the ith person will arrive to see the flowers.
Return an integer array answer of size n, where answer[i] is the number of flowers that are in full bloom when the ith person arrives.
+
Example 1:
+ +
+Input: flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], poeple = [2,3,7,11] +Output: [1,2,2,2] +Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. +For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +
+Input: flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], poeple = [3,3,2] +Output: [2,2,1] +Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. +For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104
+ flowers[i].length == 2
+ 1 <= starti <= endi <= 109
+ 1 <= people.length <= 5 * 104
+ 1 <= people[i] <= 109
+
1095. Find in Mountain Array
Hard
(This problem is an interactive problem.)
+ +You may recall that an array arr is a mountain array if and only if:
-
+
arr.length >= 3
+ - There exists some
iwith0 < i < arr.length - 1such that: +-
+
arr[0] < arr[1] < ... < arr[i - 1] < arr[i]
+ arr[i] > arr[i + 1] > ... > arr[arr.length - 1]
+
+
Given a mountain array mountainArr, return the minimum index such that mountainArr.get(index) == target. If such an index does not exist, return -1.
You cannot access the mountain array directly. You may only access the array using a MountainArray interface:
-
+
MountainArray.get(k)returns the element of the array at indexk(0-indexed).
+ MountainArray.length()returns the length of the array.
+
Submissions making more than 100 calls to MountainArray.get will be judged Wrong Answer. Also, any solutions that attempt to circumvent the judge will result in disqualification.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: array = [1,2,3,4,5,3,1], target = 3 +Output: 2 +Explanation: 3 exists in the array, at index=2 and index=5. Return the minimum index, which is 2.+ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: array = [0,1,2,4,2,1], target = 3
+Output: -1
+Explanation: 3 does not exist in the array, so we return -1.
+
+
++
Constraints:
+ +-
+
3 <= mountain_arr.length() <= 104
+ 0 <= target <= 109
+ 0 <= mountain_arr.get(index) <= 109
+
746. Min Cost Climbing Stairs
Easy
You are given an integer array cost where cost[i] is the cost of ith step on a staircase. Once you pay the cost, you can either climb one or two steps.
You can either start from the step with index 0, or the step with index 1.
Return the minimum cost to reach the top of the floor.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: cost = [10,15,20] +Output: 15 +Explanation: You will start at index 1. +- Pay 15 and climb two steps to reach the top. +The total cost is 15. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: cost = [1,100,1,1,1,100,1,1,100,1] +Output: 6 +Explanation: You will start at index 0. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 2. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 4. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 6. +- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach index 7. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 9. +- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach the top. +The total cost is 6. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= cost.length <= 1000
+ 0 <= cost[i] <= 999
+
746. Min Cost Climbing Stairs
Easy
You are given an integer array cost where cost[i] is the cost of ith step on a staircase. Once you pay the cost, you can either climb one or two steps.
You can either start from the step with index 0, or the step with index 1.
Return the minimum cost to reach the top of the floor.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: cost = [10,15,20] +Output: 15 +Explanation: You will start at index 1. +- Pay 15 and climb two steps to reach the top. +The total cost is 15. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: cost = [1,100,1,1,1,100,1,1,100,1] +Output: 6 +Explanation: You will start at index 0. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 2. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 4. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 6. +- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach index 7. +- Pay 1 and climb two steps to reach index 9. +- Pay 1 and climb one step to reach the top. +The total cost is 6. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
2 <= cost.length <= 1000
+ 0 <= cost[i] <= 999
+
Given two Binary Search Trees. Find the nodes that are common in both of them, ie- find the intersection of the two BSTs.
+Note: Return the common nodes in sorted order.
+Example 1:
+Input: +BST1: + 5 + / \ + 1 10 + / \ / + 0 4 7 + \ + 9 +BST2: + 10 + / \ + 7 20 + / \ + 4 9 +Output: 4 7 9 10 + ++
Example 2:
+Input:
+BST1:
+ 10
+ / \
+ 2 11
+ / \
+ 1 3
+BST2:
+ 2
+ / \
+ 1 3
+Output: 1 2 3
+
+Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function findCommon() that takes roots of the two BSTs as input parameters and returns a list of integers containing the common nodes in sorted order.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N1 + N2) where N1 and N2 are the sizes of the 2 BSTs.
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(H1 + H2) where H1 and H2 are the heights of the 2 BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= Number of Nodes <= 105
1 <= Node data <= 109
2742. Painting the Walls
Hard
You are given two 0-indexed integer arrays, cost and time, of size n representing the costs and the time taken to paint n different walls respectively. There are two painters available:
-
+
- A paid painter that paints the
ithwall intime[i]units of time and takescost[i]units of money.
+ - A free painter that paints any wall in
1unit of time at a cost of0. But the free painter can only be used if the paid painter is already occupied.
+
Return the minimum amount of money required to paint the n walls.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: cost = [1,2,3,2], time = [1,2,3,2] +Output: 3 +Explanation: The walls at index 0 and 1 will be painted by the paid painter, and it will take 3 units of time; meanwhile, the free painter will paint the walls at index 2 and 3, free of cost in 2 units of time. Thus, the total cost is 1 + 2 = 3. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: cost = [2,3,4,2], time = [1,1,1,1] +Output: 4 +Explanation: The walls at index 0 and 3 will be painted by the paid painter, and it will take 2 units of time; meanwhile, the free painter will paint the walls at index 1 and 2, free of cost in 2 units of time. Thus, the total cost is 2 + 2 = 4. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= cost.length <= 500
+ cost.length == time.length
+ 1 <= cost[i] <= 106
+ 1 <= time[i] <= 500
+
Given a Binary Search Tree, modify the given BST such that it is balanced and has minimum possible height. Return the balanced BST.
+Example1:
+Input: + 30 + / + 20 + / + 10+
Output: + 20 + / \ + 10 30 +
Example2:
+Input:
+ 4
+ /
+ 3
+ /
+ 2
+ /
+ 1
+Output:
+ 3 3 2
+ / \ / \ / \
+ 1 4 OR 2 4 OR 1 3
+ \ / \
2 1 4
+
Your Task:
The task is to complete the function buildBalancedTree() which takes root as the input argument and returns the root of tree after converting the given BST into a balanced BST with minimum possible height. The driver code will print the height of the updated tree in output itself.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Here N denotes total number of nodes in given BST.
Constraints:
1 <= N <= 105
1 <= Node data <= 109
1269. Number of Ways to Stay in the Same Place After Some Steps
Hard
You have a pointer at index 0 in an array of size arrLen. At each step, you can move 1 position to the left, 1 position to the right in the array, or stay in the same place (The pointer should not be placed outside the array at any time).
Given two integers steps and arrLen, return the number of ways such that your pointer is still at index 0 after exactly steps steps. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: steps = 3, arrLen = 2 +Output: 4 +Explanation: There are 4 differents ways to stay at index 0 after 3 steps. +Right, Left, Stay +Stay, Right, Left +Right, Stay, Left +Stay, Stay, Stay ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: steps = 2, arrLen = 4 +Output: 2 +Explanation: There are 2 differents ways to stay at index 0 after 2 steps +Right, Left +Stay, Stay ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: steps = 4, arrLen = 2 +Output: 8 ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= steps <= 500
+ 1 <= arrLen <= 106
+
119. Pascal's Triangle II
Easy
Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth (0-indexed) row of the Pascal's triangle.
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
+ +
++
Example 1:
+Input: rowIndex = 3 +Output: [1,3,3,1] +
Example 2:
+Input: rowIndex = 0 +Output: [1] +
Example 3:
+Input: rowIndex = 1 +Output: [1,1] ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
+
+
Follow up: Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(rowIndex) extra space?
119. Pascal's Triangle II
Easy
Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth (0-indexed) row of the Pascal's triangle.
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
+ +
++
Example 1:
+Input: rowIndex = 3 +Output: [1,3,3,1] +
Example 2:
+Input: rowIndex = 0 +Output: [1] +
Example 3:
+Input: rowIndex = 1 +Output: [1,1] ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
+
+
Follow up: Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(rowIndex) extra space?
Given a directed graph, determine whether a vertex j is reachable from another vertex i for all vertex pairs (i, j) in the given graph. Here, vertex j is reachable from another vertex i means that there is a path from vertex i to j. The reachability matrix is called the transitive closure of a graph. The directed graph is represented by an adjacency matrix where there are N vertices.
+Example 1:
+Input: N = 4 +graph = {{1, 1, 0, 1}, + {0, 1, 1, 0}, + {0, 0, 1, 1}, + {0, 0, 0, 1}} +Output: {{1, 1, 1, 1}, + {0, 1, 1, 1}, + {0, 0, 1, 1}, + {0, 0, 0, 1}} +Explanation:+
The output list shows the reachable indexes.
Example 2:
+Input: N = 3
+graph = {{1, 0, 0},
+ {0, 1, 0},
+ {0, 0, 1}}
+Output: {{1, 0, 0},
+ {0, 1, 0},
+ {0, 0, 1}}
+Explanation:
The output list shows the reachable indexes.
+Your Task:
You do not need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function transitiveClosure() which takes an integer N and a 2D array graph(adjacency matrix of the graph) as input parameters and returns the transitive closure of the graph in the form of 2D array.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N3)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Constraints:
1 ≤ N ≤ 100
1361. Validate Binary Tree Nodes
Medium
You have n binary tree nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 where node i has two children leftChild[i] and rightChild[i], return true if and only if all the given nodes form exactly one valid binary tree.
If node i has no left child then leftChild[i] will equal -1, similarly for the right child.
Note that the nodes have no values and that we only use the node numbers in this problem.
+ ++
Example 1:
+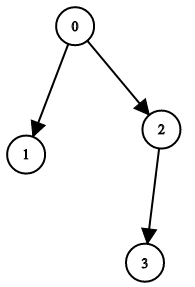 +
+Input: n = 4, leftChild = [1,-1,3,-1], rightChild = [2,-1,-1,-1] +Output: true ++ +
Example 2:
+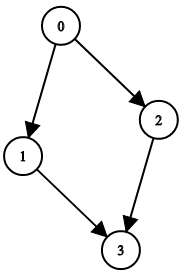 +
+Input: n = 4, leftChild = [1,-1,3,-1], rightChild = [2,3,-1,-1] +Output: false ++ +
Example 3:
+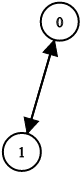 +
+Input: n = 2, leftChild = [1,0], rightChild = [-1,-1] +Output: false ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
n == leftChild.length == rightChild.length
+ 1 <= n <= 104
+ -1 <= leftChild[i], rightChild[i] <= n - 1
+
A directed graph of V vertices and E edges is given in the form of an adjacency list adj. Each node of the graph is labelled with a distinct integer in the range 0 to V - 1.
+ +A node is a terminal node if there are no outgoing edges. A node is a safe node if every possible path starting from that node leads to a terminal node.
+ +You have to return an array containing all the safe nodes of the graph. The answer should be sorted in ascending order.
+ +Example 1:
+ +Input: + ++ ++Output: +2 4 5 6 +Explanation: +The given graph is shown above. +Nodes 5 and 6 are terminal nodes as there are no +outgoing edges from either of them. +Every path starting at nodes 2, 4, 5, and 6 all +lead to either node 5 or 6. +
Example 2:
+ +Input: + ++ ++Output: +3 +Explanation: +Only node 3 is a terminal node, and every path +starting at node 3 leads to node 3. +
Your Task:
+You don't need to read or print anything. Your task is to complete the function eventualSafeNodes() which takes an integer V denoting no. of vertices and adj denoting adjacency list of the graph and returns an array of safe nodes.
Expected Time Complexity: O(V + E)
+ +Expected Space Complexity: O(V)
+ +Constraints:
+ +-
+
- 1 <= V <= 104 +
- 0 <= E <= 104 +
- The graph won't contain self loops. +
- Each node in the graph has a distinct value in the range 0 to V - 1. +
2050. Parallel Courses III
Hard
You are given an integer n, which indicates that there are n courses labeled from 1 to n. You are also given a 2D integer array relations where relations[j] = [prevCoursej, nextCoursej] denotes that course prevCoursej has to be completed before course nextCoursej (prerequisite relationship). Furthermore, you are given a 0-indexed integer array time where time[i] denotes how many months it takes to complete the (i+1)th course.
You must find the minimum number of months needed to complete all the courses following these rules:
+ +-
+
- You may start taking a course at any time if the prerequisites are met. +
- Any number of courses can be taken at the same time. +
Return the minimum number of months needed to complete all the courses.
+ +Note: The test cases are generated such that it is possible to complete every course (i.e., the graph is a directed acyclic graph).
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +
+
+
+Input: n = 3, relations = [[1,3],[2,3]], time = [3,2,5] +Output: 8 +Explanation: The figure above represents the given graph and the time required to complete each course. +We start course 1 and course 2 simultaneously at month 0. +Course 1 takes 3 months and course 2 takes 2 months to complete respectively. +Thus, the earliest time we can start course 3 is at month 3, and the total time required is 3 + 5 = 8 months. ++ +
Example 2:
+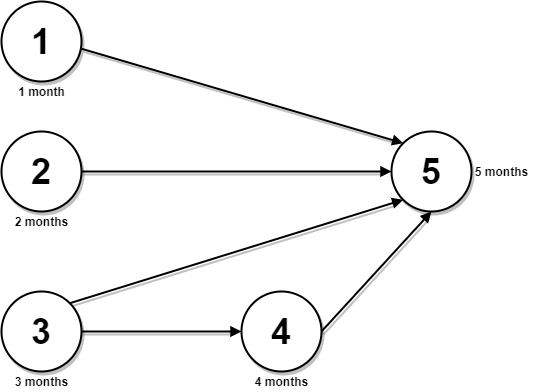 +
+
+
+Input: n = 5, relations = [[1,5],[2,5],[3,5],[3,4],[4,5]], time = [1,2,3,4,5] +Output: 12 +Explanation: The figure above represents the given graph and the time required to complete each course. +You can start courses 1, 2, and 3 at month 0. +You can complete them after 1, 2, and 3 months respectively. +Course 4 can be taken only after course 3 is completed, i.e., after 3 months. It is completed after 3 + 4 = 7 months. +Course 5 can be taken only after courses 1, 2, 3, and 4 have been completed, i.e., after max(1,2,3,7) = 7 months. +Thus, the minimum time needed to complete all the courses is 7 + 5 = 12 months. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= n <= 5 * 104
+ 0 <= relations.length <= min(n * (n - 1) / 2, 5 * 104)
+ relations[j].length == 2
+ 1 <= prevCoursej, nextCoursej <= n
+ prevCoursej != nextCoursej
+ - All the pairs
[prevCoursej, nextCoursej]are unique.
+ time.length == n
+ 1 <= time[i] <= 104
+ - The given graph is a directed acyclic graph. +
You will be given an array arr of integers of length N. You can construct an integer from two integers by treating the integers as strings, and then concatenating them. For example, 19 and 4 can be used to construct 194 and 419.
+The task is to find whether it’s possible to construct an integer using all the digits of these numbers such that it would be divisible by 3.
If it is possible then print 1 and if not print 0.
Example 1:
+Input: N = 3
+arr = {40, 50, 90}
+Output: 1
+Explanation: One such number is 405090.
+Example 2:
+Input: N = 2
+arr = {1, 4}
+Output: 0
+Explanation: The numbers we can form
+are 14 and 41. But neither of them are
+divisible by 3.
+Your Task:
You do not need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function isPossible() which takes N and arr as input parameters and returns 1 if we can form a number by the digits of the given number, that would be divisible by 3, otherwise returns 0.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
1 ≤ N, arr[i] ≤ 105
844. Backspace String Compare
Easy
Given two strings s and t, return true if they are equal when both are typed into empty text editors. '#' means a backspace character.
Note that after backspacing an empty text, the text will continue empty.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: s = "ab#c", t = "ad#c" +Output: true +Explanation: Both s and t become "ac". ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: s = "ab##", t = "c#d#" +Output: true +Explanation: Both s and t become "". ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: s = "a#c", t = "b" +Output: false +Explanation: s becomes "c" while t becomes "b". ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= s.length, t.length <= 200
+ sandtonly contain lowercase letters and'#'characters.
+
+
Follow up: Can you solve it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
341. Flatten Nested List Iterator
Medium
You are given a nested list of integers nestedList. Each element is either an integer or a list whose elements may also be integers or other lists. Implement an iterator to flatten it.
Implement the NestedIterator class:
-
+
NestedIterator(List<NestedInteger> nestedList)Initializes the iterator with the nested listnestedList.
+ int next()Returns the next integer in the nested list.
+ boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there are still some integers in the nested list andfalseotherwise.
+
Your code will be tested with the following pseudocode:
+ +initialize iterator with nestedList +res = [] +while iterator.hasNext() + append iterator.next() to the end of res +return res ++ +
If res matches the expected flattened list, then your code will be judged as correct.
+
Example 1:
+ +Input: nestedList = [[1,1],2,[1,1]] +Output: [1,1,2,1,1] +Explanation: By calling next repeatedly until hasNext returns false, the order of elements returned by next should be: [1,1,2,1,1]. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nestedList = [1,[4,[6]]] +Output: [1,4,6] +Explanation: By calling next repeatedly until hasNext returns false, the order of elements returned by next should be: [1,4,6]. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nestedList.length <= 500
+ - The values of the integers in the nested list is in the range
[-106, 106].
+
Given a positive integer N., The task is to find the value of where function F(i) for the number i is defined as the sum of all divisors of i.
Example 1:
+Input: +N = 4 +Output: +15 +Explanation: +F(1) = 1 +F(2) = 1 + 2 = 3 +F(3) = 1 + 3 = 4 +F(4) = 1 + 2 + 4 = 7 +ans = F(1) + F(2) + F(3) + F(4) + = 1 + 3 + 4 + 7 + = 15+
Example 2:
+Input: +N = 5 +Output: +21 +Explanation: +F(1) = 1 +F(2) = 1 + 2 = 3 +F(3) = 1 + 3 = 4 +F(4) = 1 + 2 + 4 = 7 +F(5) = 1 + 5 = 6 +ans = F(1) + F(2) + F(3) + F(4) + F(5) + = 1 + 3 + 4 + 7 + 6 + = 21+
Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function sumOfDivisors() which takes an integer N as an input parameter and returns an integer.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
1 <= N <= 106
1425. Constrained Subsequence Sum
Hard
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the maximum sum of a non-empty subsequence of that array such that for every two consecutive integers in the subsequence, nums[i] and nums[j], where i < j, the condition j - i <= k is satisfied.
A subsequence of an array is obtained by deleting some number of elements (can be zero) from the array, leaving the remaining elements in their original order.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [10,2,-10,5,20], k = 2 +Output: 37 +Explanation: The subsequence is [10, 2, 5, 20]. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [-1,-2,-3], k = 1 +Output: -1 +Explanation: The subsequence must be non-empty, so we choose the largest number. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [10,-2,-10,-5,20], k = 2 +Output: 23 +Explanation: The subsequence is [10, -2, -5, 20]. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= k <= nums.length <= 105
+ -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
239. Sliding Window Maximum
Hard
You are given an array of integers nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position.
Return the max sliding window.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 +Output: [3,3,5,5,6,7] +Explanation: +Window position Max +--------------- ----- +[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 + 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 + 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 + 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 + 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 + 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7 ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [1], k = 1 +Output: [1] ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 105
+ -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+ 1 <= k <= nums.length
+
1425. Constrained Subsequence Sum
Hard
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the maximum sum of a non-empty subsequence of that array such that for every two consecutive integers in the subsequence, nums[i] and nums[j], where i < j, the condition j - i <= k is satisfied.
A subsequence of an array is obtained by deleting some number of elements (can be zero) from the array, leaving the remaining elements in their original order.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [10,2,-10,5,20], k = 2 +Output: 37 +Explanation: The subsequence is [10, 2, 5, 20]. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [-1,-2,-3], k = 1 +Output: -1 +Explanation: The subsequence must be non-empty, so we choose the largest number. ++ +
Example 3:
+ +Input: nums = [10,-2,-10,-5,20], k = 2 +Output: 23 +Explanation: The subsequence is [10, -2, -5, 20]. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= k <= nums.length <= 105
+ -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
The problem is to count all the possible paths from top left to bottom right of an MxN matrix with the constraints that from each cell you can either move to right or down.
+Return answer modulo 109+7.
+Example 1:
+Input:
+M = 3 and N = 3
+Output: 6
+Explanation:
+Let the given input 3*3 matrix is filled
+as such:
+A B C
+D E F
+G H I
+The possible paths which exists to reach
+'I' from 'A' following above conditions
+are as follows:ABCFI, ABEHI, ADGHI, ADEFI,
+ADEHI, ABEFI
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
+M = 1 and N = 4
+Output: 1
+Explanation:
+There is only one direction to go in,
and thus, there is only one path possible.
+Your Task
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function numberOfPaths() which takes the integer M and integer N as input parameters and returns an integer, the number of paths.
Expected Time Complexity: O(M)
Expected Space Complexity: O(1)
Constraints:
1 ≤ N ≤ 108
1 ≤ M ≤ 105
1793. Maximum Score of a Good Subarray
Hard
You are given an array of integers nums (0-indexed) and an integer k.
The score of a subarray (i, j) is defined as min(nums[i], nums[i+1], ..., nums[j]) * (j - i + 1). A good subarray is a subarray where i <= k <= j.
Return the maximum possible score of a good subarray.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,4,3,7,4,5], k = 3 +Output: 15 +Explanation: The optimal subarray is (1, 5) with a score of min(4,3,7,4,5) * (5-1+1) = 3 * 5 = 15. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [5,5,4,5,4,1,1,1], k = 0 +Output: 20 +Explanation: The optimal subarray is (0, 4) with a score of min(5,5,4,5,4) * (4-0+1) = 4 * 5 = 20. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 105
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 104
+ 0 <= k < nums.length
+
1793. Maximum Score of a Good Subarray
Hard
You are given an array of integers nums (0-indexed) and an integer k.
The score of a subarray (i, j) is defined as min(nums[i], nums[i+1], ..., nums[j]) * (j - i + 1). A good subarray is a subarray where i <= k <= j.
Return the maximum possible score of a good subarray.
+ ++
Example 1:
+ +Input: nums = [1,4,3,7,4,5], k = 3 +Output: 15 +Explanation: The optimal subarray is (1, 5) with a score of min(4,3,7,4,5) * (5-1+1) = 3 * 5 = 15. ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: nums = [5,5,4,5,4,1,1,1], k = 0 +Output: 20 +Explanation: The optimal subarray is (0, 4) with a score of min(5,5,4,5,4) * (4-0+1) = 4 * 5 = 20. ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
1 <= nums.length <= 105
+ 1 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 104
+ 0 <= k < nums.length
+
342. Power of Four
Easy
Given an integer n, return true if it is a power of four. Otherwise, return false.
An integer n is a power of four, if there exists an integer x such that n == 4x.
+
Example 1:
+Input: n = 16 +Output: true +
Example 2:
+Input: n = 5 +Output: false +
Example 3:
+Input: n = 1 +Output: true ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
-231 <= n <= 231 - 1
+
+Follow up: Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
342. Power of Four
Easy
Given an integer n, return true if it is a power of four. Otherwise, return false.
An integer n is a power of four, if there exists an integer x such that n == 4x.
+
Example 1:
+Input: n = 16 +Output: true +
Example 2:
+Input: n = 5 +Output: false +
Example 3:
+Input: n = 1 +Output: true ++
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
-231 <= n <= 231 - 1
+
+Follow up: Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
515. Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, return an array of the largest value in each row of the tree (0-indexed).
+
Example 1:
+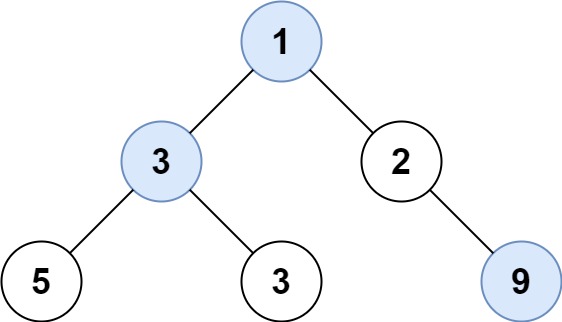 +
+Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] +Output: [1,3,9] ++ +
Example 2:
+ +Input: root = [1,2,3] +Output: [1,3] ++ +
+
Constraints:
+ +-
+
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[0, 104].
+ -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
+
Given a set of N items, each with a weight and a value, represented by the array w and val respectively. Also, a knapsack with weight limit W.
The task is to fill the knapsack in such a way that we can get the maximum profit. Return the maximum profit.
Note: Each item can be taken any number of times.
Example 1:
+Input:
N = 2
W = 3
+val = {1, 1}
+wt = {2, 1}
+Output:
3
+Explanation:
+1.Pick the 2nd element thrice.
+2.Total profit = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3. Also the total weight = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 which is <= 3.
+
+Example 2:
+Input:
N = 4
W = 8
+val[] = {6, 1, 7, 7}
+wt[] = {1, 3, 4, 5}
+Output:
48
+Explanation:
The optimal choice is to pick the 1st element 8 times.
+Your Task:
You do not need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function knapSack() which takes the values N, W and the arrays val and wt as input parameters and returns the maximum possible value.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N*W)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(W)
Constraints:
1 ≤ N, W ≤ 1000
1 ≤ val[i], wt[i] ≤ 100